What Is a Search Engine? A Guide to Understanding the Compass of the Digital Universe
Discover the secrets of crawling, indexing, and ranking by search engines. How do Google, Bing, and Yandex work? Everything you need to know about next-generation AI-powered search technologies and the future of SEO is in this guide. You will find answers to all your questions related to topic What Is a Search Engine? A Guide to Understanding the Compass of the Digital Universe in the continuation of the text.

Why Are Search Engines So Important?
How Do Search Engines Work? 3 Fundamental Steps
1. Crawling
2. Indexing
3. Ranking
The 5 Most Popular Search Engines and Their Features
1. Google
2. Microsoft Bing
3. Yandex
4. DuckDuckGo
5. Baidu
The Future of Search Engines: Artificial Intelligence and Semantic Search
The Importance of Search Engines for Businesses: What Is SEO?
Conclusion: The Compass of the Digital Universe
The internet is like a vast library containing billions of pages. In this library, the magical tools that allow you to reach the specific information you're looking for within seconds are called search engines. These technologies, indispensable in the digital age, have fundamentally changed the way we access information and become one of the most essential building blocks shaping today's world.
As Piar Medya, we examine in-depth for you how this complex yet fascinating system works and why it is vitally important for your digital presence.
Why Are Search Engines So Important?
The primary function of search engines is to discover, interpret, and present the most relevant answers to users' queries from publicly available content on the internet. Their importance lies in the following points:
- Instant Access to Information: They offer the ability to access any kind of information in seconds, from an academic paper to a recipe, and from the latest news to a product's price.
- Creating Economic Value: They are one of the most effective channels for businesses to reach potential customers and promote their products and services. They are the lifeblood of every sector, from e-commerce to local services.
- Decision-Making Processes: Users always use search engines to research before purchasing a product, choosing a service, or going somewhere. Thus, search results become a critical decision-making mechanism.
How Do Search Engines Work? 3 Fundamental Steps
Behind the apparent simplicity of a search engine lies incredibly complex and ever-evolving technology. Its operating principle consists of three fundamental stages. Understanding how the process works is the foundation of search engine optimization (SEO) strategies. Here are those three magical steps:
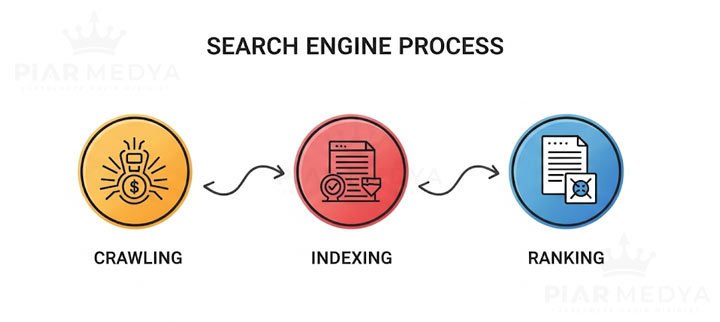
1. Crawling
Search engines continuously crawl the internet using automated programs called "spiders" or "bots." Spiders navigate from one web page to another by following links. They discover newly published or updated pages. How frequently a site is crawled depends on factors such as the site's authority, how often its content is updated, and its technical infrastructure.
2. Indexing
The content discovered during the crawling phase is recorded in the search engine's vast database, i.e., its "index." Indexing is not just about storing the page's URL. The search engine analyzes and interprets the page's content (texts, headings, images, videos), its structure, and its metadata. After understanding what the page is about, it categorizes the page into relevant topics before adding it to the index. If a page is not added to the index, it will never appear in search results.
3. Ranking
When a user enters a search query, the most complex phase begins. The search engine uses complex algorithms that consider hundreds of factors to find the most appropriate and highest quality answers to the user's query from the billions of pages in its index. Although the exact composition of these algorithms is a trade secret, the main ranking factors are as follows:
- Relevance: How well the page's content, headings, and meta descriptions match the search query.
- Authority and Trustworthiness (E-E-A-T): How reliable and expert the site is. Reference links (backlinks) from other high-quality sites are very important here.
- User Experience: Metrics such as whether the page is mobile-friendly, how fast it loads, and how easily users can navigate the site.
- Content Quality and Freshness: Whether the content is original, comprehensive, accurate, and up to date.
For the most authoritative information on how this process works, you can review Google's "How Search Works" page.
The 5 Most Popular Search Engines and Their Features
Although market shares vary worldwide, some search engines stand out by a large margin. Here are the giants of the digital world:
1. Google
Google, the undisputed market leader, is known for its simplicity, speed, and highly advanced algorithm. Beyond being just a search engine, it offers an integrated ecosystem of vertical search services such as Maps, Images, News, and Scholar. Its continually updated algorithm always keeps the goal of delivering the most relevant results to users at its core.
2. Microsoft Bing
Bing, Microsoft's search engine, stands out particularly for its visual search capabilities. With rich images and video previews on its search results page, it offers a distinct user experience. In recent years, its collaboration with OpenAI has integrated AI-powered chat and content creation features into the search engine, making it a serious competitor to Google.
3. Yandex
Yandex, which holds a significant market share especially in countries like Russia and Turkey, is very strong in local services and its mapping service (Yandex Maps). Its advanced algorithms for understanding language and local culture make it popular in these regions. It is also known for offering free and advanced analytics tools for site owners, such as Yandex Metrica.
4. DuckDuckGo
Known by the slogan "The search engine that doesn't track you", DuckDuckGo commits to not tracking users' searches or storing personal data. It is the most popular alternative for those who value privacy. It compiles search results from other search engines' APIs and its own crawler.
5. Baidu
Baidu, known as China's Google, holds a dominant advantage in the Chinese market. It has complex algorithms that deeply understand the Mandarin language and China's digital ecosystem. It encompasses numerous services such as music, maps, and cloud storage. Unless you are a global enterprise, you are unlikely to encounter it, but it's a key player to know when understanding the global market.
The Future of Search Engines: Artificial Intelligence and Semantic Search
Search engines are not static systems. With updates like the MUVERA 2025 Core Update, the future has already begun to take shape. We expect the following trends to dominate:
- Generative AI: As seen in projects like Google's SGE (Search Generative Experience), search engines now do more than just list links; they generate summarized, conversational responses to your queries.
- Semantic Search: Search engines are now focusing on understanding the "meaning" and "intent" behind a query rather than just keywords. As a result, they provide more accurate results for searches conducted in natural language.
- Voice and Visual Search: Thanks to smart assistants and smartphone cameras, "keyboard-free" search is becoming increasingly common. Users are searching by voice or by taking a photo of an object.
These developments further underscore the importance of web standards. Topics such as structured data and accessibility will form the foundation of future SEO. To learn more about standards, it's important to follow resources from the World Wide Web Consortium (W3C).
The Importance of Search Engines for Businesses: What Is SEO?
If you are a business owner, search engines are the main gateway through which potential customers reach you. When your customers search for a product or service, your website needs to appear before your competitors. This is where Search Engine Optimization (SEO) comes into play.
SEO is the collection of technical and strategic efforts made to make your website and content easier for search engines to understand and to have them rank you higher because they deem your content valuable. At Piar Media, our SEO services aim to increase your brand's visibility and authority in the digital world. For more information, you can review this comprehensive resource explaining what SEO is.
Conclusion: The Compass of the Digital Universe
Search engines are the gateway to information in the modern world and the engine of the digital economy. Understanding how they work and how they will evolve in the future is a crucial competency for both individuals and businesses. They are not just tools; they are indispensable compasses that help us find our way in the digital universe. To stay informed about the search technologies of the future, following technology publications like Wired will broaden your horizon.






